Mitochondrial structure in cells of the Neuro-2a WT neuronal lineage
Description of the photo
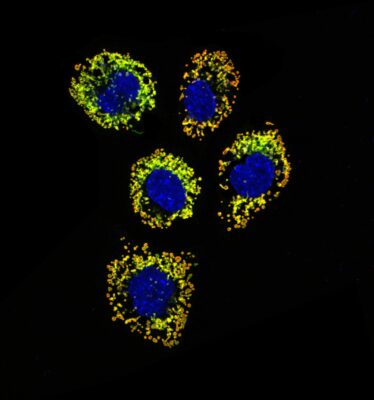
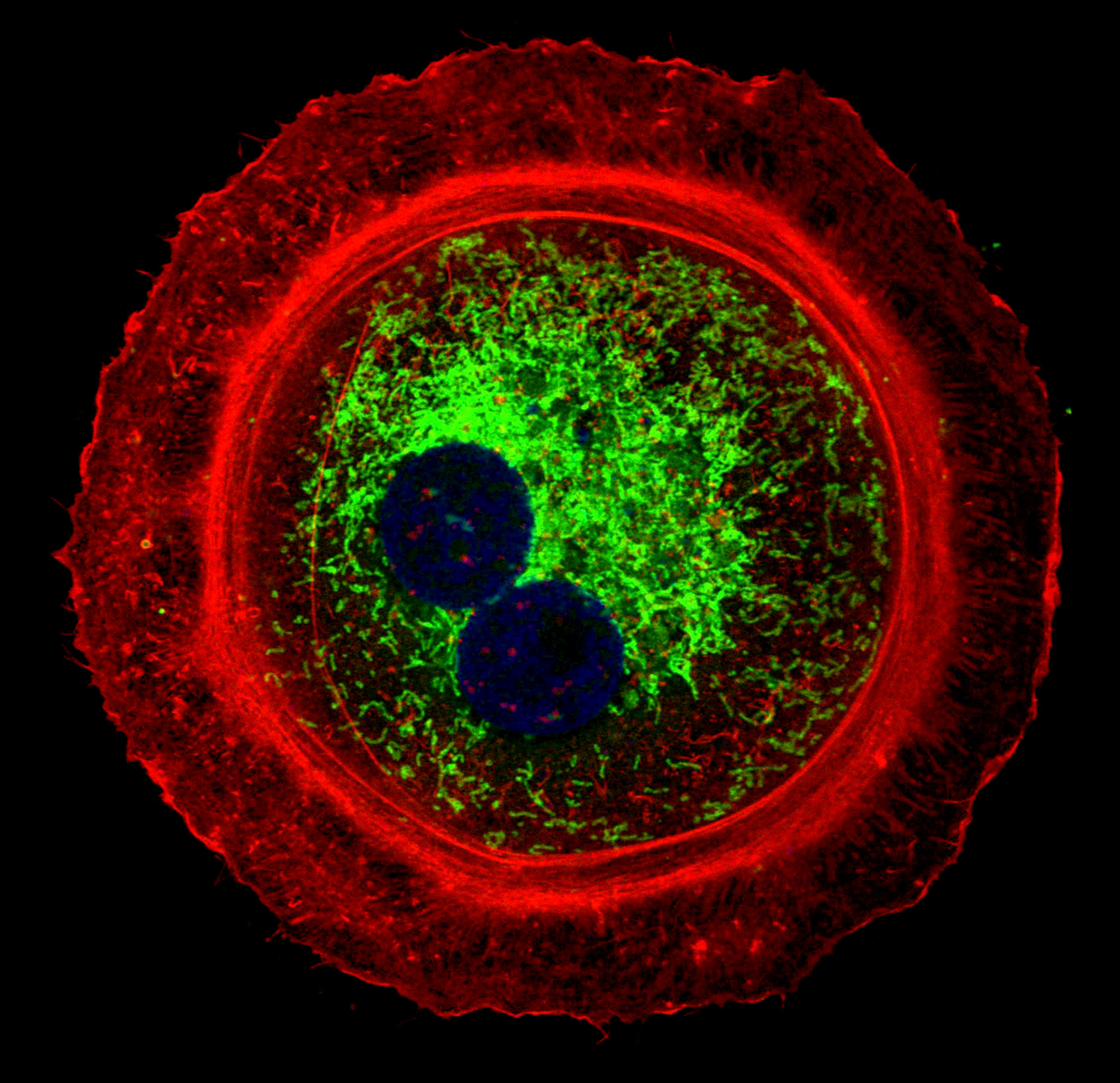
The image shows neuroblastoma cells neuro-2a (N2a), two fluorescent antibodies were used to mark the outer membranes (TOM20) in green and the matrices (HSP70) in red of the mitochondria, the DAPI to show the cell nuclei in blue. This line was used as a control to analyze the mitochondrial morphology between two neuronal lines N2a-WT and N2a TBC1D24-KO where the TBC1D24 gene was completely deleted by Crispr-cas9, the aim is to identify the effect of this mutation on the structure or even the mitochondrial function. Today, however, we know that the TBC1D24 protein plays a crucial role in neuronal maturation and development, the exact physiological role of this protein is poorly understood. What is known, however, is that mutations in the TBC1D24 protein are involved in several hereditary neurological diseases including DOORS syndrome, which is a rare autosomal recessive genetic disorder. This syndrome shows phenotypic similarities with mitochondrial diseases. Precisely, the results obtained indicate that distinct mutations associated with DOORS syndrome cause specific changes in the structure of mitochondria in primary fibroblasts of patients with DOORS syndrome. And since mitochondria are regulated by dynamic changes in their architecture, our goal is to determine whether mitochondrial alterations caused by the TBC1D24 mutation could contribute to the pathology of DOORS syndrome.
Author
Name: Benhammouda Sara
Affiliation: UQTR
Edition: 2020